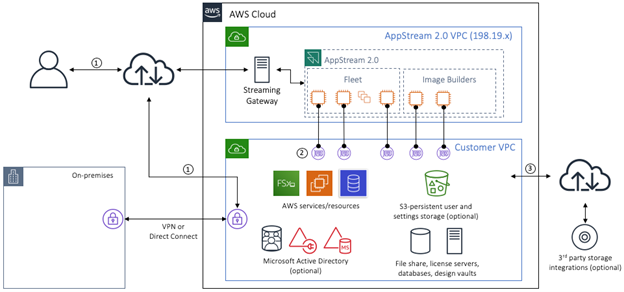
and secure your cloud.
Cloud Migration:
With the increasing benefits of using the cloud, more and more organizations are migrating over their
workloads. The key driver for this migration is the adoption of technology across every business vertical.
With technology adoption, the investment in resources increases significantly.
Cloud migration is the process of moving all digital resources to the cloud from either on-premise
deployments or from another cloud. Formulating a robust cloud migration strategy is the first step
toward migration. A cloud migration strategy is essential for both companies moving their legacy
systems to the cloud for the first time and existing cloud users looking to optimize their investment.
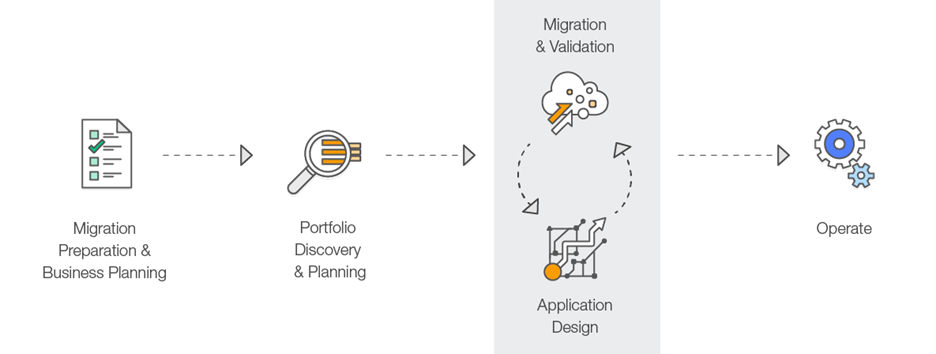
First stage of migration involves analyzing the application dependencies and the requirements, think
about the business objectives, the roadmap, risk posture, cost associated with project. During this
phase, you evaluate your app inventory in order to plan what you should migrate to the new
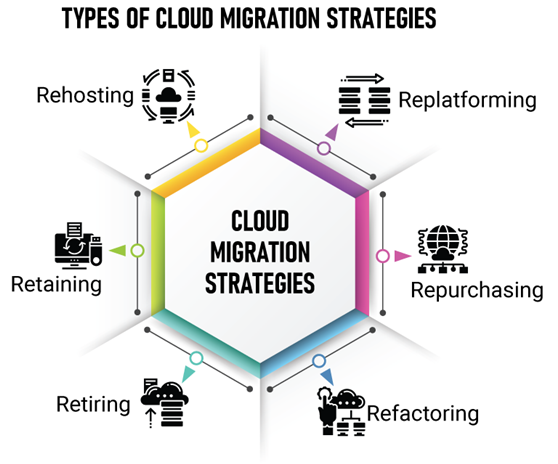
environment. AWS 6R philosophy ( Rehost, Replatforming, Repurchasing, Refactoring, Retiring,
Retaining) of cloud migration is also good reference while deciding on migration strategy.
We offer solutions that ease the process of application migration and modernization, enable building
new cloud-native applications, and transform your infrastructure. The cloud’s agility is realized through
automation. We carefully determine which processes to be automated and establish new processes that
can take advantage of automation and manage services offered by cloud player. This helps customer in
making resources free from day to day mundane tasks and focus on delivering business value. We also
assist customers to adjust their internal processes so that they’re able to embrace technological change.

We ensure that customer get maximum value for cloud investments. We offer a set of services with monitoring strategy to ensure all critical aspects of cloud functioning and performance are monitored with help of cloud native tools. Data-driven insights into how cloud environment is performing is key to effective cloud governance.
Cloud Database Migration:
Database migrations to the cloud is very critical process of any cloud migration process and is often time-consuming and complex. With Enaxa’s in-house expertise in Cloud Migration and cloud Database Migration Services, customers can successfully migrate databases along with the application to the public cloud easily and seamlessly. Today, customers have option of migrating just the database to another cloud platform without going for full stack migration. This means you can get best from cloud of your choice without affecting application performance and user experience.
Enaxa helps in implementing the selected databases offered by the cloud provider of choice. We have helped
customers to adopt public cloud platforms effectively & efficiently. The new age Relational databases are
available in different flavors and do not require administration efforts. Customers can opt for multitude
of databases like No-SQL, Graph offered by cloud players. We help customers choose the right database by
going through multiple exercises and creating a decision matrix. Once a decision is made, we help with
implementations considering critical aspects, such as security, availability and performance..
AWS Migration Process

Cloud Security
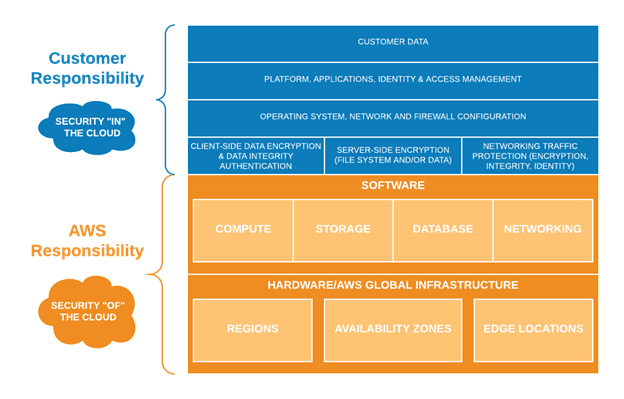
The Shared Responsibility Model is a security and compliance framework that outlines
the responsibilities of cloud service providers (CSPs) and customers for securing every aspect of the cloud
environment, including hardware, infrastructure, endpoints, data, configurations, settings, operating
system (OS), network controls and access rights.
In its simplest terms, the Shared Responsibility Model dictates that the cloud provider—such as
Amazon Web Service (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP)—must monitor and respond
to security threats related to the cloud itself and its underlying infrastructure. Meanwhile, end
users, including individuals and companies, are responsible for protecting data and other assets
they store in any cloud environment.

Many organizations are moving from on-premises to cloud with a ‘lift and shift’ approach. The tools and processes used to manage and monitor those applications and infrastructures are no longer valid in cloud environment. In such scenarios, Applications and services hosted in cloud are susceptible to different kinds of threats from the outside. Cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and brute-force attacks are some examples. Without proper security management, company’s sensitive information and database credentials are at risk.
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Implementing multi-factor authentication for access to the cloud platform and data
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Regularly monitoring and auditing cloud resources for unauthorized access or suspicious activity
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Establishing incident response plans and procedures for dealing with security breaches
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates

It is also important to carefully evaluate and choose a reputable cloud service provider that has
strong security measures in place and is compliant with industry standards such as SOC 2, ISO 27001,
and PCI DSS.
In addition, organizations should also implement a cloud governance strategy which includes policies,
standards, procedures and guidelines that provide oversight and management of the cloud environment.
This should be integrated with the organizations overall IT governance, risk management and
compliance strategy
Cloud security can be divided into three main layers: Application, Network and Workload.
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Web application firewalls (WAFs):
For protecting web-based applications from common attacks such
as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS)
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Identity and access management (IAM):
Very critical as many times the bad actors get access to
employee credentials and subsequently to company’s cloud resources and data.
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Encryption for protecting data in transit and at rest
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) for monitoring and analyzing security-related data
keyboard_double_arrow_right
API security for securing the communication between applications
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Virtual private networks (VPNs) for encrypting communications between cloud-based resources and on-premises networks
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Cloud access security brokers (CASBs) for controlling access to cloud resources and data
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Firewalls for controlling inbound and outbound traffic to cloud-based resources
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Network segmentation for isolating different parts of the network to limit the scope of a security breach
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Container security for securing the deployment and management of containerized workloads
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Serverless security for securing serverless functions and applications
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Virtual machine security for securing virtual machines and their associated operating systems
keyboard_double_arrow_right
File integrity monitoring for detecting and alerting on any unauthorized changes to files
keyboard_double_arrow_right
Vulnerability management for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in cloud-based resources
Cloud Data Warehouse
Today, many business-critical applications like databases, ERPs, and Marketing applications have all
moved to cloud. Since, all business critical data resides on the cloud, companies need a data warehouse
that can seamlessly store the data from all the different cloud-based applications. This is where Cloud
Data Warehouse becomes critical business need.
A Cloud Data Warehouse is a database that is delivered as a managed service in the public cloud and is
optimized for analytics, scale, and usability. Cloud-based data warehouses allow businesses to focus on
running their businesses rather than managing a server room, and they enable business intelligence
teams to deliver faster and better insights due to improved access, scalability, and performance.
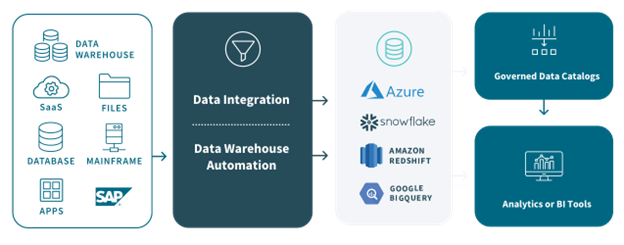
The first step is to get a complete picture of data and its source. We understand data attributes, relationships and dependencies.
Once data is ingested into the data lake, data is cleansed, profiled as appropriate. Also , de-duplication, verification and integrity testing happens at this stage.
Once we have identified the right data, we ingest the data into cloud data lake. That usually starts with an initial load from an on-premises data warehouse followed by an incremental load to capture change data capture from the database.
Once the data is in the cloud data warehouse, data consumers
may want to further slice and dice datasets. Customers can
ontinue using the visual designer to build business logic.
TIt's important to note that the security approach for
each layer may vary depending on the cloud provider, service or infrastructure
you are using, and the specific use case of the organization.
Overall, cloud security is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring,
testing, and updating to keep pace with the latest threats and best practices.
Our experts can help customers integrate the appropriate controls, orchestrate
workload deployment and establish effective threat management.